Brake Shoe Assembly Design and Performance Enhancements
 2025.02.05
2025.02.05
 Industry News
Industry News
Design Considerations for Brake Shoe Assemblies
The design of a brake shoe assembly must consider several factors to ensure optimal performance and reliability:
Friction Material: The choice of friction material is one of the most important aspects of brake shoe design. Traditionally, brake shoes were lined with asbestos, but due to safety and environmental concerns, modern assemblies use non-asbestos materials such as ceramic, metallic, or organic compounds. These materials offer high friction coefficients, long-lasting durability, and resistance to heat buildup, which is crucial during extended braking periods.
Brake Shoe Shape and Size: The shape and size of the brake shoe must be carefully designed to ensure proper contact with the brake drum. Too small, and the shoes may not provide enough friction; too large, and they may cause excessive wear or drag. Precision in design ensures balanced performance, minimizing heat buildup and wear.
Ventilation and Heat Dissipation: As braking generates heat, effective ventilation within the brake shoe assembly is necessary to dissipate that heat quickly and prevent overheating. Modern designs often feature vented or slotted brake shoes, which enhance airflow and improve cooling efficiency.
Performance Enhancements in Brake Shoe Assemblies
Recent advancements have focused on improving the performance of brake shoe assemblies, making them more effective and durable:
High-Performance Friction Materials: Many modern brake shoes are equipped with advanced composite materials that offer superior heat resistance, improved wear properties, and reduced brake fade. These materials provide consistent stopping power across a wide range of temperatures and driving conditions.
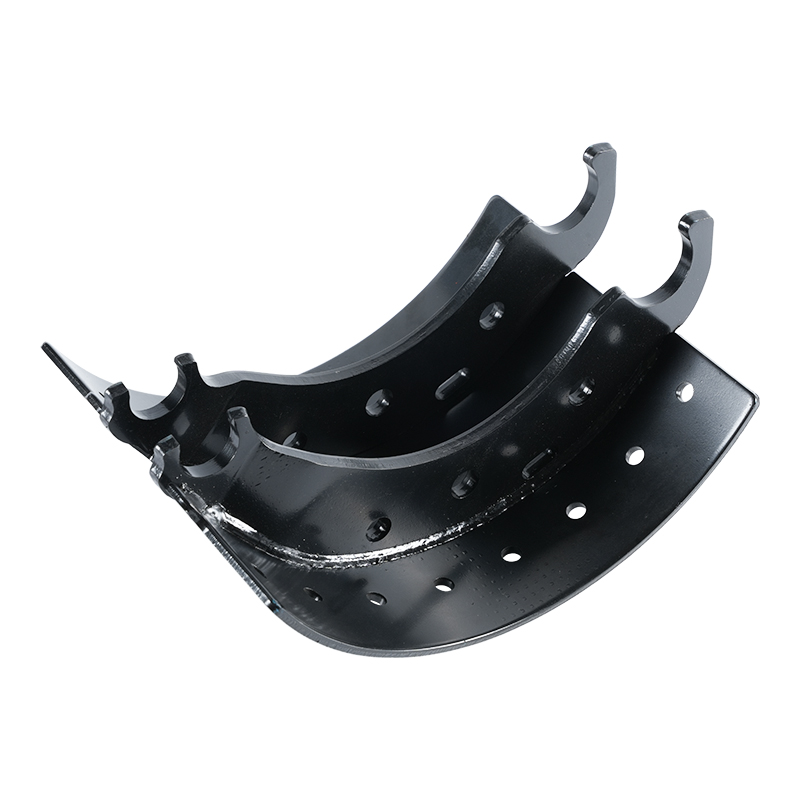

Self-Adjusting Systems: Modern brake shoe assemblies often include self-adjusting mechanisms that automatically compensate for wear and maintain the correct position of the brake shoes. This eliminates the need for manual adjustments and helps maintain consistent brake performance over time.
Corrosion-Resistant Coatings: The metal components of brake shoe assemblies, such as the shoes and the hold-down clips, are often coated with corrosion-resistant materials to prevent rust and extend the lifespan of the parts. This is especially important in regions where vehicles are exposed to harsh weather conditions and road salts.
Impact of Design on Vehicle Performance
The performance of brake shoe assemblies directly affects the overall handling and safety of a vehicle. Well-designed brake shoe assemblies ensure smooth and effective braking, reduce wear on other components of the braking system (such as the drum), and enhance the vehicle’s ability to stop quickly in emergency situations.
In addition to improving safety, optimized brake shoe assemblies can also contribute to improved fuel efficiency. Excessive brake drag can reduce a vehicle’s fuel economy, so ensuring that the brake shoes retract properly and do not stay in contact with the drum when not in use is crucial for minimizing unnecessary resistance.

 Eng
Eng  中文简体
中文简体









