Brake Shoe Assembly: A Deep Dive into Manufacturing and Quality Control
 2025.01.15
2025.01.15
 Industry News
Industry News
The Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing of brake shoe assemblies involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the parts meet rigorous performance standards. Here are the main steps involved in producing a brake shoe assembly:
Material Selection: The first step in the process is selecting the right materials for the brake shoes and friction material. The brake shoes are typically made of steel or cast iron, while the friction material is made from a composite of organic or semi-metallic compounds. The materials are selected for their ability to withstand heat, wear, and the stresses that occur during braking.
Stamping and Shaping: The brake shoes are stamped from metal sheets using precision machines. This process shapes the metal into the desired arc, ensuring a precise fit within the brake drum. The stamping process also creates the mounting holes and slots required for the brake shoe assembly.
Bonding the Friction Material: The next step is bonding the friction material to the metal brake shoe. This can be done through an adhesive bonding process or by using rivets. The friction material is precisely shaped and fitted to match the curvature of the brake shoe. The bond must be strong to prevent any separation during operation.
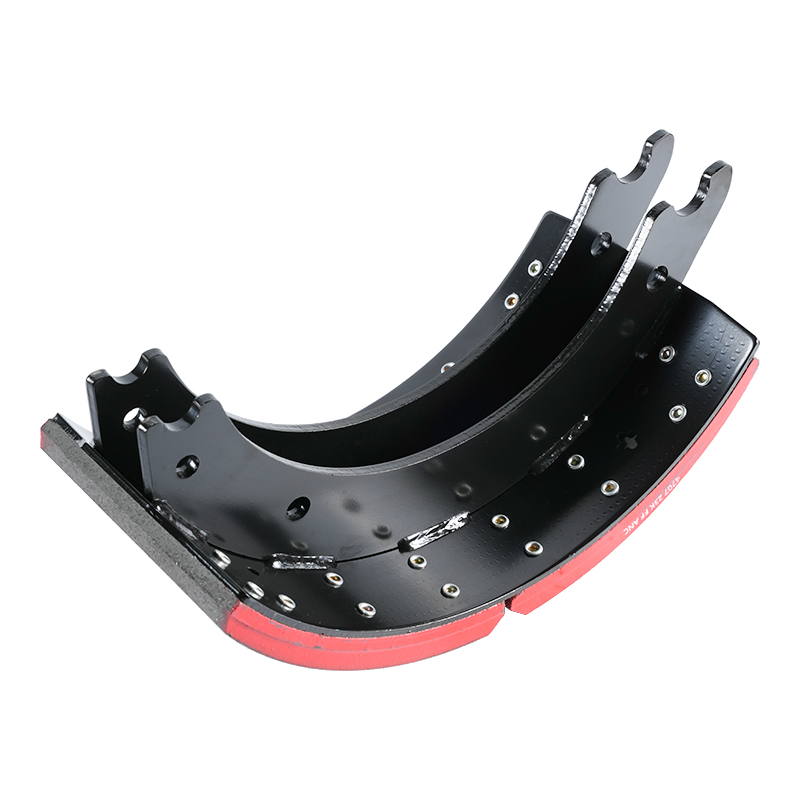

Assembly and Installation of Springs: Springs are attached to the brake shoes, securing them into the correct position. These springs are crucial for maintaining the proper tension and ensuring the shoes return to their resting position after the brake pedal is released.
Adjustment Mechanisms: An automatic adjuster mechanism is often incorporated into the assembly. This ensures that the brake shoes remain at the correct distance from the brake drum, compensating for wear and ensuring even braking performance.
Testing and Quality Control: After the assembly, each brake shoe unit is thoroughly tested for performance and safety. Testing may include checking the brake shoe’s fit, ensuring the friction material is securely bonded, and testing for smooth operation. Brake shoe assemblies are also subjected to environmental tests, such as heat resistance, to ensure they can withstand the extreme temperatures that occur during braking.
Quality Control Measures
Quality control is vital in the manufacturing process of brake shoe assemblies. Since these components are directly related to vehicle safety, any defects or substandard materials can lead to catastrophic failure. Key quality control steps include:
Visual Inspection: Each brake shoe is inspected for defects, such as cracks, dents, or imperfections in the friction material.
Dimensional Checks: All critical dimensions are checked to ensure the brake shoe fits perfectly within the brake drum.
Performance Testing: Brake shoe assemblies are tested for performance under a range of conditions, including extreme temperatures and repeated braking cycles.
Durability Testing: To ensure the brake shoes last the life of the vehicle, they are subjected to rigorous wear and tear tests.

 Eng
Eng  中文简体
中文简体









