The Evolution of Brake Shoe Assemblies: From Early Designs to Modern Innovations
 2025.01.22
2025.01.22
 Industry News
Industry News
Early Brake Shoe Designs
The concept of brake shoes dates back to the early days of automobiles. The earliest vehicles relied on simple mechanical brake systems, often using leather or wood as the friction material. These rudimentary designs were effective but had limitations, especially in terms of durability and stopping power.
As vehicles grew faster and more powerful, the need for more efficient and reliable braking systems became apparent. In response, the automotive industry began to develop metal-based brake shoes. These brake shoes were paired with drums, which served as the braking surface. This early drum brake system was more effective than its predecessors and became the standard for many vehicles during the 20th century.
Advancements in Materials and Design
The 1950s and 1960s saw significant advancements in materials used for brake shoes. Instead of using pure metal, manufacturers began to use composite friction materials, which provided better performance and durability. These materials included combinations of metals, resins, and other compounds, which allowed the brake shoes to last longer and perform better under high temperatures.
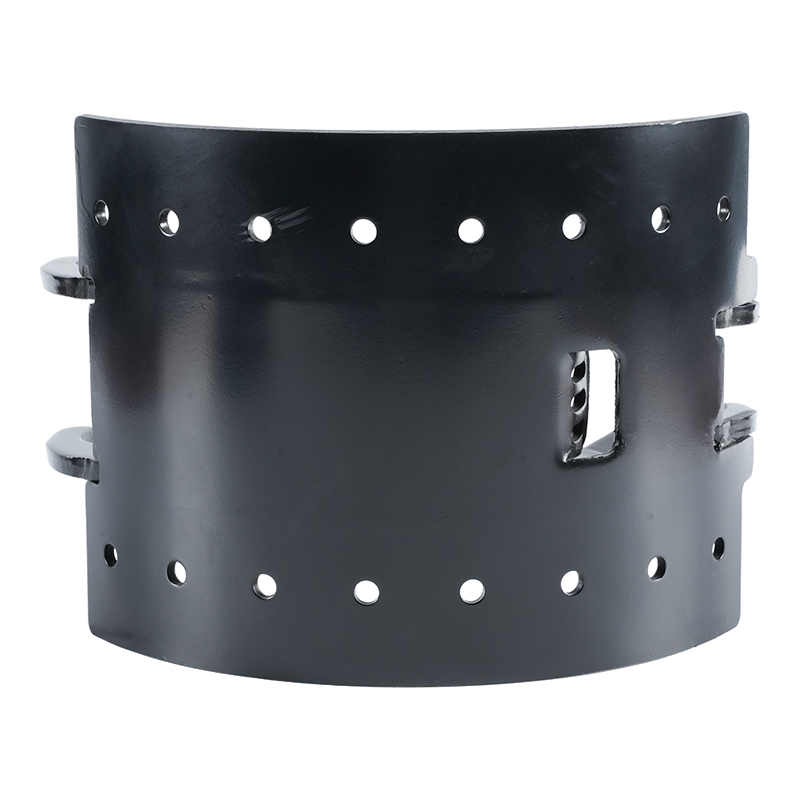

During the same period, the design of the brake shoe assembly was refined. Springs, clips, and adjusters were added to enhance the shoe’s operation and ensure proper alignment with the brake drum. These innovations made the braking system more efficient and reliable, significantly improving vehicle safety.
Modern Innovations in Brake Shoe Assemblies
Today, brake shoe assemblies are much more advanced, incorporating the latest materials and technology to meet the high standards of modern vehicles. Key innovations in brake shoe assemblies include:
Ceramic Friction Materials: Many modern brake shoes use ceramic-based friction materials, which offer superior braking performance while reducing noise and dust. These materials also generate less heat, increasing the longevity of the brake system.
Self-Adjusting Mechanisms: Modern brake shoe assemblies often feature self-adjusting mechanisms, which ensure the proper distance between the brake shoes and the drum. This improves braking efficiency and reduces the need for manual adjustments.
Integrated Sensors: Some brake shoe assemblies now feature sensors that monitor the thickness of the friction material. These sensors alert drivers when it’s time to replace the brake shoes, preventing wear-related failures.
Eco-Friendly Designs: With growing concerns over environmental impact, manufacturers have been focusing on developing more eco-friendly brake shoes. This includes using non-toxic materials for the friction compound and designing shoes that generate less dust and particulate pollution.

 Eng
Eng  中文简体
中文简体









